Genitourinary (GU)
Author
Katrina Collins, MD
Summary of clinical history
53-year-old female with well-circumscribed right renal mass, partial nephrectomy was performed
Gross findings
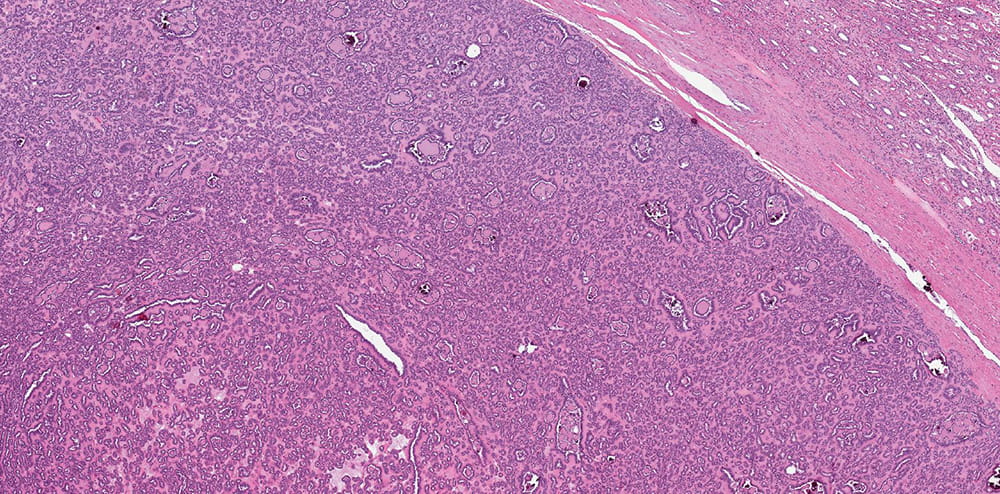
4.7 cm tan, well-circumscribed and focally hemorrhagic mass, confined to kidney
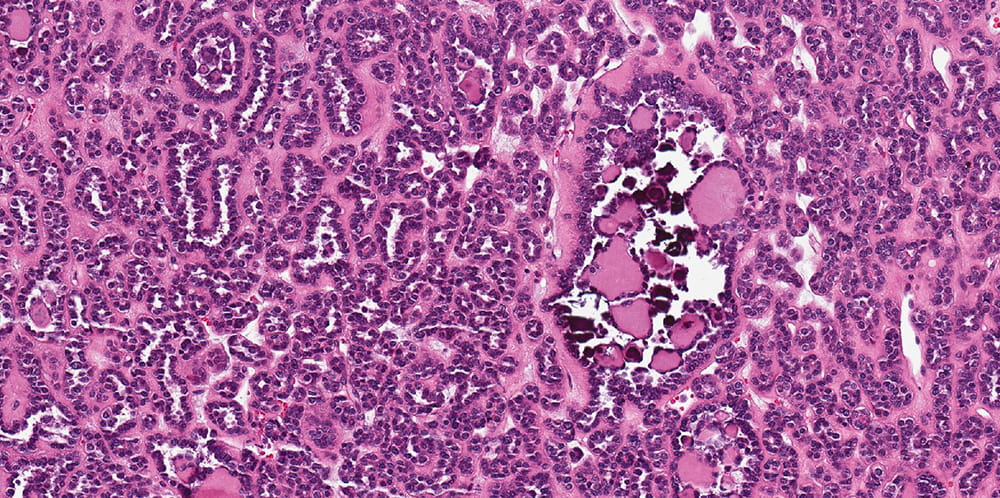
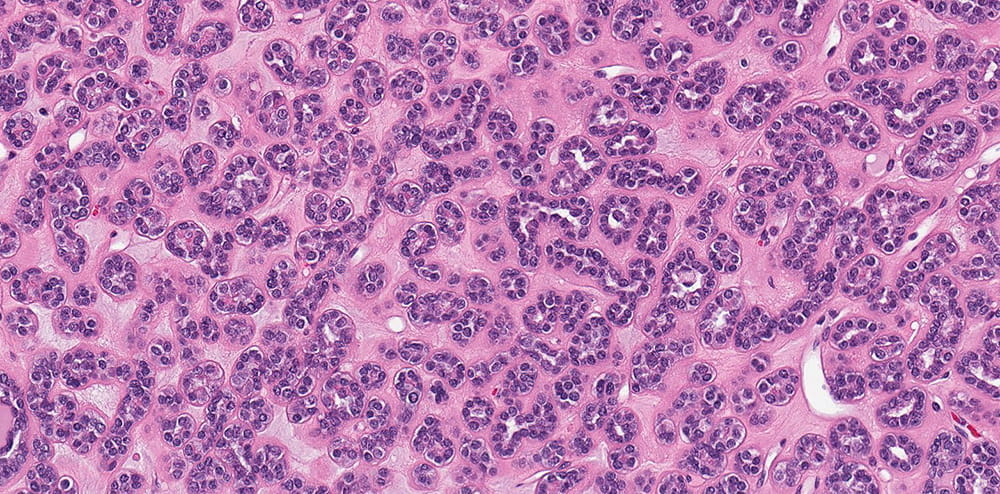
Microscopic findings
The tumor is well-circumscribed but not encapsulated. Tumor is composed of tightly packed tubules. Tumor nuclei are round or oval with occasional grooves and no obvious nucleoli are present and the cell cytoplasm is scant. In some areas, curvilinear tubules imparting papillary appearance are seen. Psammomatous calcifications are abundant. Click for larger versions.
Immunohistochemical findings
Positive: WT1, CD57, BRAF, PAX8
Negative: CK7, AMACR